1.8 Resize
Home and Learn - Free Excel VBA Course
9.2 Add the Code for the User Form Button
In the previous lesson, you created a form with a button and a textbox. In this lesson, you'll see how to add the code for the button.
A button has to do something when it's clicked. What we'll do is to get a number from the textbox and transfer it to a cell on the spreadsheet. The form will then unload itself. And all on the click of a button.
To get at the code stub for a button, simply double click it on the form. When you do, you'll see this:

The name of our button was changed to cmdGetNumber. You'll see this name in two places: at the very top, in a dropdown list, and just after Sub in the coding window.
If you click the dropdown list at the top, you'll see this:

The items on the list are all the controls you have placed on the form, as well as the form itself. Each item has something called an event attached to it. You can see a list of all the events by clicking the second dropdown list:
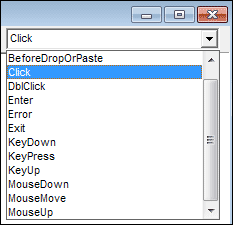
An event is what happens when you do something with a control. For a button, this "something" is usually a click. But you can also write code for what happens when the button is double clicked, when the mouse is over the button, or any events on the list above. By double clicking the button on the form, the Editor automatically takes you into the Click event, which is what you'll want most of the time.
The code stub for the click event looks like this:
Private Sub cmdGetNumber_Click( )
End Sub
This is a Private Sub. The name of the Sub is cmdGetNumber. After an underscore, comes the name of the event, Click. After the event, you'll see a pair of round brackets. Any code you want to execute when the button is clicked goes between the two lines above.
To manipulate a control on a form with code this syntax is this:
Control_Name.Property
You can access a control from any other control. So the button can access certain properties of a textbox and the textbox can access certain properties of the button. We want to get at the text in the textbox when the button is clicked. We also want to place this text into a cell on a spreadsheet. The code, then, is this:
ActiveCell.Value = txtValue.Text
To the right of the equal sign we have this:
txtValue.Text
We changed the name of our textbox to txtValue. This is the control name. The property of the textbox we want to access is the Text property. As its name suggest, this will get you the text in the textbox. If you want to set a value for the textbox, the code goes to the left of the equal sign:
txtValue.Text = "Some Text"
So it's just like the variable assignment you've been doing so far. Here, we're assigning the string "Some Text" to the Text property of the textbox control.
There are lots and lots of properties of a control that you can manipulate. As soon as you type a dot after the control name, you should see a list appear:
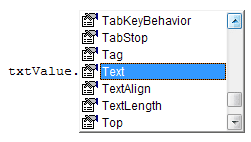
A lot of the items in the above list are also in the Properties area in the VBA Editor. For example, the Top, Left, Height and Width properties. This means that you can change these properties with code, as well as from the Editor. If you wanted to, you could change the Top and Left properties of the textbox like this when the button is clicked:
txtValue.Left = 10
txtValue.Top = 10
When you change a property from an event like a button click you are said to be making changes "on the fly", or making changes "at runtime".
So be aware that any properties in the Properties area in the Editor can also be changed with code.
Time to try it out, though. Click anywhere inside of your code. Now press F5 to run the form. Type anything you like into your textbox. Now click your button. You should see whatever is in the textbox appear in the active cell on your spreadsheet:

However, when the button is clicked, we'd also like the form to go away. This is done with the Unload keyword.
Unload form_name
As well as the form name after a space, you can also type the keyword Me:
Unload Me
Add that line to your code and it will look like this:
Private Sub cmdGetNumber_Click()
ActiveCell.Value = txtValue.Text
Unload Me
End Sub
Try it out again. This time, when you click the button the form will unload. Go back to your spreadsheet and you'll see whatever you typed in the textbox is also in the active cell.
Type a single quote before each of the two lines of code, thereby commenting them out. Now try these exercises.
Exercise
Write code to change the Height and Width of the textbox when the button is
clicked. Change the Height to 35 and the Width to 75.
Exercise
Write code to change the background colour of the form (BackColor) when the
button is clicked. Try some of these after the equal sign of your property:
vbRed
vbBlue
vbBlack
vbWhite
You can also try an RGB color:
RGB(255, 100, 12)
Exercise
Write code to change the Caption property of the button when it is clicked.
Change the property to GO.
Exercise
Write code to transfer the Caption property of the button to the textbox when
the button is clicked
In the next lesson, you'll learn about the different ways you can launch your User Forms.
Next Lesson: 9.3 Launch Form from Excel >